Page 3 - LN
P. 3
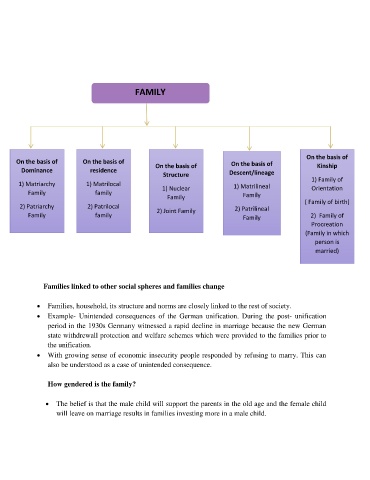
FAMILY
On the basis of
On the basis of On the basis of On the basis of On the basis of Kinship
Dominance residence
Structure Descent/lineage
1) Family of
1) Matriarchy 1) Matrilocal 1) Nuclear 1) Matrilineal Orientation
Family family Family
Family ( Family of birth)
2) Patriarchy 2) Patrilocal
2) Joint Family 2) Patrilineal
Family family Family 2) Family of
Procreation
(Family in which
person is
married)
Families linked to other social spheres and families change
Families, household, its structure and norms are closely linked to the rest of society.
Example- Unintended consequences of the German unification. During the post- unification
period in the 1930s Germany witnessed a rapid decline in marriage because the new German
state withdrewall protection and welfare schemes which were provided to the families prior to
the unification.
With growing sense of economic insecurity people responded by refusing to marry. This can
also be understood as a case of unintended consequence.
How gendered is the family?
The belief is that the male child will support the parents in the old age and the female child
will leave on marriage results in families investing more in a male child.