Page 3 - Microsoft Word - Home assignment 19 Directing Meaning Importance
P. 3
organizations, certain pieces are checked at random for quality. This is known as
sample checking.
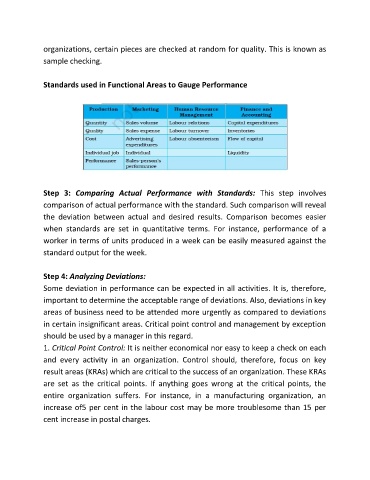
Standards used in Functional Areas to Gauge Performance
Step 3: Comparing Actual Performance with Standards: This step involves
comparison of actual performance with the standard. Such comparison will reveal
the deviation between actual and desired results. Comparison becomes easier
when standards are set in quantitative terms. For instance, performance of a
worker in terms of units produced in a week can be easily measured against the
standard output for the week.
Step 4: Analyzing Deviations:
Some deviation in performance can be expected in all activities. It is, therefore,
important to determine the acceptable range of deviations. Also, deviations in key
areas of business need to be attended more urgently as compared to deviations
in certain insignificant areas. Critical point control and management by exception
should be used by a manager in this regard.
1. Critical Point Control: It is neither economical nor easy to keep a check on each
and every activity in an organization. Control should, therefore, focus on key
result areas (KRAs) which are critical to the success of an organization. These KRAs
are set as the critical points. If anything goes wrong at the critical points, the
entire organization suffers. For instance, in a manufacturing organization, an
increase of5 per cent in the labour cost may be more troublesome than 15 per
cent increase in postal charges.