Page 7 - Home Assignment-Price determination
P. 7
In the above diagram the equilibrium price ‘OP’ and quantity ‘OQ’
is determined at point ‘E’ where market demand = market supply.
Due to increase in supply the supply curve shifts right ward to
|
resulting an excess supply situation in the market by EF.
In order to overcome the excess supply situation, the price level
|
will fall, it will lead to contraction in supply from F to and
|
expansion in demand from E to .
|
Finally, the equilibrium price will fall to and quantity will
|
increase to respectively.
Special cases: -
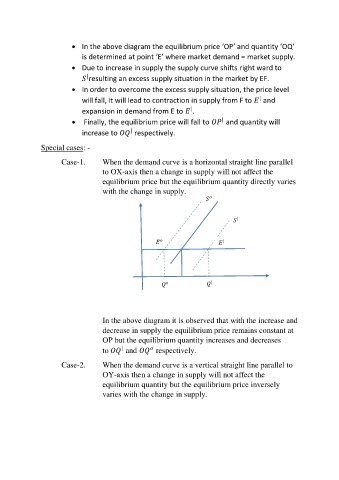
Case-1. When the demand curve is a horizontal straight line parallel
to OX-axis then a change in supply will not affect the
equilibrium price but the equilibrium quantity directly varies
with the change in supply.
S
Y
|
Pri
ce
|
E
P D
X
|
O Q Quantity demanded
and quantity supplied
In the above diagram it is observed that with the increase and
decrease in supply the equilibrium price remains constant at
OP but the equilibrium quantity increases and decreases
|
to and respectively.
Case-2. When the demand curve is a vertical straight line parallel to
OY-axis then a change in supply will not affect the
equilibrium quantity but the equilibrium price inversely
varies with the change in supply.