Page 6 - 2.Lesson_notes-Asexual_Reproduction_2
P. 6
Such methods also make possible the propagation of plants such as banana,
orange, rose and jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
All plants produced are genetically similar enough to the parent plant.
Disadvantages
These methods can be used only in plants which cannot produce seeds or
produce non-viable seeds.
The new plants look exactly like their parent plants and reveal no variations.
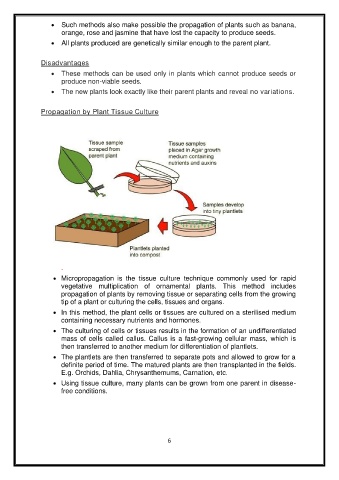
Propagation by Plant Tissue Culture
.
Micropropagation is the tissue culture technique commonly used for rapid
vegetative multiplication of ornamental plants. This method includes
propagation of plants by removing tissue or separating cells from the growing
tip of a plant or culturing the cells, tissues and organs.
In this method, the plant cells or tissues are cultured on a sterilised medium
containing necessary nutrients and hormones.
The culturing of cells or tissues results in the formation of an undifferentiated
mass of cells called callus. Callus is a fast-growing cellular mass, which is
then transferred to another medium for differentiation of plantlets.
The plantlets are then transferred to separate pots and allowed to grow for a
definite period of time. The matured plants are then transplanted in the fields.
E.g. Orchids, Dahlia, Chrysanthemums, Carnation, etc.
Using tissue culture, many plants can be grown from one parent in disease-
free conditions.
6