Page 3 - 2.Lesson_notes-Asexual_Reproduction_2
P. 3
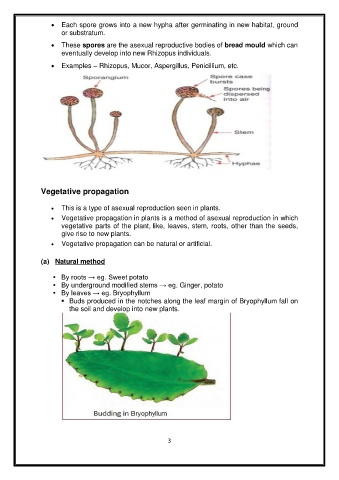
Each spore grows into a new hypha after germinating in new habitat, ground
or substratum.
These spores are the asexual reproductive bodies of bread mould which can
eventually develop into new Rhizopus individuals.
Examples – Rhizopus, Mucor, Aspergillus, Penicillium, etc.
Vegetative propagation
This is a type of asexual reproduction seen in plants.
Vegetative propagation in plants is a method of asexual reproduction in which
vegetative parts of the plant, like, leaves, stem, roots, other than the seeds,
give rise to new plants.
Vegetative propagation can be natural or artificial.
(a) Natural method
• By roots → eg. Sweet potato
• By underground modified stems → eg. Ginger, potato
• By leaves → eg. Bryophyllum
Buds produced in the notches along the leaf margin of Bryophyllum fall on
the soil and develop into new plants.
3