Page 4 - 2.Lesson_notes-Asexual_Reproduction_2
P. 4
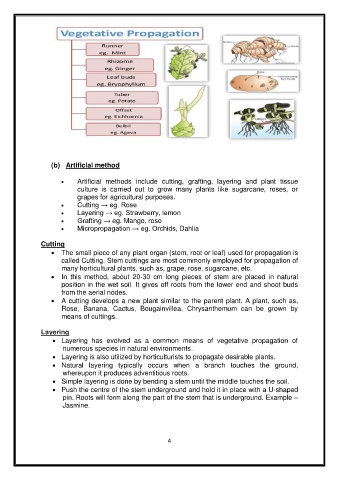
(b) Artificial method
Artificial methods include cutting, grafting, layering and plant tissue
culture is carried out to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses, or
grapes for agricultural purposes.
Cutting → eg. Rose
Layering → eg. Strawberry, lemon
Grafting → eg. Mango, rose
Micropropagation → eg. Orchids, Dahlia
Cutting
The small piece of any plant organ (stem, root or leaf) used for propagation is
called Cutting. Stem cuttings are most commonly employed for propagation of
many horticultural plants, such as, grape, rose, sugarcane, etc.
In this method, about 20-30 cm long pieces of stem are placed in natural
position in the wet soil. It gives off roots from the lower end and shoot buds
from the aerial nodes.
A cutting develops a new plant similar to the parent plant. A plant, such as,
Rose, Banana, Cactus, Bougainvillea, Chrysanthemum can be grown by
means of cuttings.
Layering
Layering has evolved as a common means of vegetative propagation of
numerous species in natural environments.
Layering is also utilized by horticulturists to propagate desirable plants.
Natural layering typically occurs when a branch touches the ground,
whereupon it produces adventitious roots.
Simple layering is done by bending a stem until the middle touches the soil.
Push the centre of the stem underground and hold it in place with a U-shaped
pin. Roots will form along the part of the stem that is underground. Example –
Jasmine.
4