Page 3 - LN
P. 3
16 Accountancy
1.5.4 Liabilities
Liabilities are obligations or debts that an enterprise has to pay at some time in
the future. They represent creditors’ claims on the firm’s assets. Both small and
big businesses find it necessary to borrow money at one time or the other, and
to purchase goods on credit. Super Bazar, for example, purchases goods for Rs.
10,000 on credit for a month from Fast Food Products on March 25, 2005. If
the balance sheet of Super Bazaar is prepared as at March 31, 2005, Fast Food
Products will be shown as creditors on the liabilities side of the balance sheet. If
Super Bazaar takes a loan for a period of three years from Delhi State Co-operative
Bank, this will also be shown as a liability in the balance sheet of Super Bazaar.
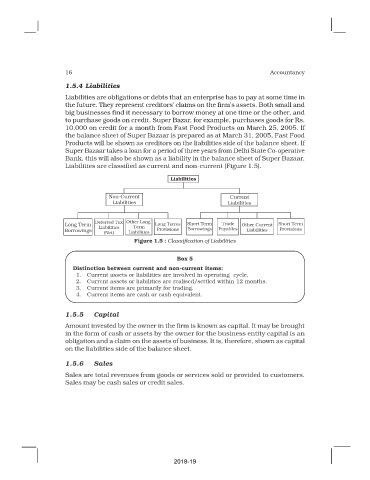
Liabilities are classified as current and non-current (Figure 1.5).
Liabilities
Non-Current Current
Liabilities Liabilities
Deferred Tax Other Long
Long Term Term Long Terms Short Term Trade Other Current Short Term
Borrowings Liabilities Provisions Borrowings Payables Liabilities Provisions
(Net) Liabilities
Figure 1.5 : Classification of Liabilities
Box 5
Distinction between current and non-current items:
1. Current assets or liabilities are involved in operating cycle.
2. Current assets or liabilities are realised/settled within 12 months.
3. Current items are primarily for trading.
4. Current items are cash or cash equivalent.
1.5.5 Capital
Amount invested by the owner in the firm is known as capital. It may be brought
in the form of cash or assets by the owner for the business entity capital is an
obligation and a claim on the assets of business. It is, therefore, shown as capital
on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
1.5.6 Sales
Sales are total revenues from goods or services sold or provided to customers.
Sales may be cash sales or credit sales.
2018-19