Page 8 - Lesson Notes - Biomolecules 1
P. 8
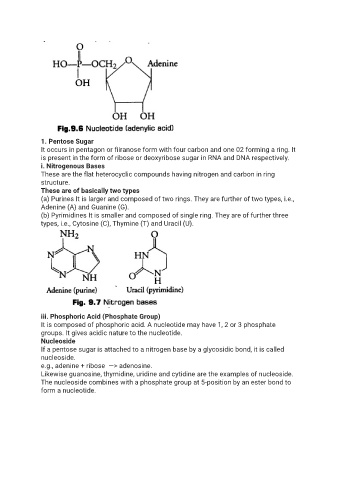
1. Pentose Sugar
It occurs in pentagon or fiiranose form with four carbon and one 02 forming a ring. It
is present in the form of ribose or deoxyribose sugar in RNA and DNA respectively.
i. Nitrogenous Bases
These are the flat heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen and carbon in ring
structure.
These are of basically two types
(a) Purines It is larger and composed of two rings. They are further of two types, i.e.,
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G).
(b) Pyrimidines It is smaller and composed of single ring. They are of further three
types, i.e., Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) and Uracil (U).
iii. Phosphoric Acid (Phosphate Group)
It is composed of phosphoric acid. A nucleotide may have 1, 2 or 3 phosphate
groups. It gives acidic nature to the nucleotide.
Nucleoside
If a pentose sugar is attached to a nitrogen base by a glycosidic bond, it is called
nucleoside.
e.g., adenine + ribose —> adenosine.
Likewise guanosine, thymidine, uridine and cytidine are the examples of nucleoside.
The nucleoside combines with a phosphate group at 5-position by an ester bond to
form a nucleotide.