Page 2 - 3. Lesson Note Ch-5 TRENDS IN THE PROPERTIES
P. 2
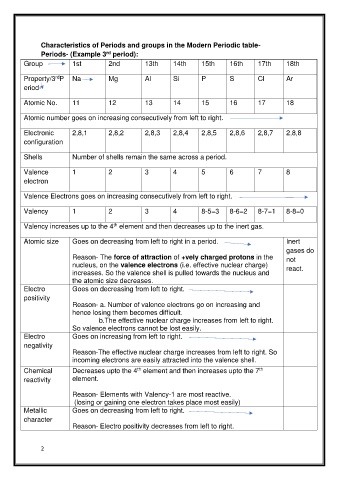
Characteristics of Periods and groups in the Modern Periodic table-
Periods- (Example 3 period):
rd
Group 1st 2nd 13th 14th 15th 16th 17th 18th
rd
Property/3 P Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
eriod-
Atomic No. 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
Atomic number goes on increasing consecutively from left to right.
Electronic 2,8,1 2,8,2 2,8,3 2,8,4 2,8,5 2,8,6 2,8,7 2,8,8
configuration
Shells Number of shells remain the same across a period.
Valence 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
electron
Valence Electrons goes on increasing consecutively from left to right.
Valency 1 2 3 4 8-5=3 8-6=2 8-7=1 8-8=0
Valency increases up to the 4 element and then decreases up to the inert gas.
th
Atomic size Goes on decreasing from left to right in a period. Inert
gases do
Reason- The force of attraction of +vely charged protons in the not
nucleus, on the valence electrons (i.e. effective nuclear charge) react.
increases. So the valence shell is pulled towards the nucleus and
the atomic size decreases.
Electro Goes on decreasing from left to right.
positivity
Reason- a. Number of valence electrons go on increasing and
hence losing them becomes difficult.
b.The effective nuclear charge increases from left to right.
So valence electrons cannot be lost easily.
Electro Goes on increasing from left to right.
negativity
Reason-The effective nuclear charge increases from left to right. So
incoming electrons are easily attracted into the valence shell.
Chemical Decreases upto the 4 element and then increases upto the 7
th
th
reactivity element.
Reason- Elements with Valency-1 are most reactive.
(losing or gaining one electron takes place most easily)
Metallic Goes on decreasing from left to right.
character
Reason- Electro positivity decreases from left to right.
2