Page 2 - 3. Lesson Note Ch-5 MODERN PERIODIC TABLE
P. 2
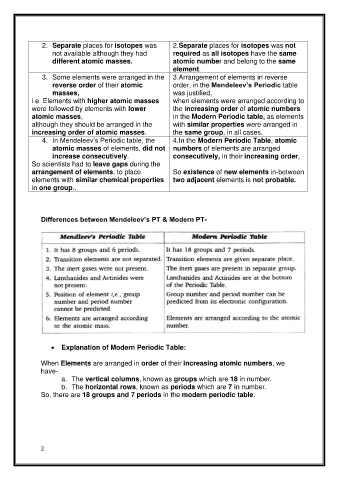
2. Separate places for isotopes was 2.Separate places for isotopes was not
not available although they had required as all isotopes have the same
different atomic masses. atomic number and belong to the same
element.
3. Some elements were arranged in the 3.Arrangement of elements in reverse
reverse order of their atomic order, in the Mendeleev’s Periodic table
masses, was justified,
i.e. Elements with higher atomic masses when elements were arranged according to
were followed by elements with lower the increasing order of atomic numbers
atomic masses, in the Modern Periodic table, as elements
although they should be arranged in the with similar properties were arranged in
increasing order of atomic masses. the same group, in all cases.
4. In Mendeleev’s Periodic table, the 4.In the Modern Periodic Table, atomic
atomic masses of elements, did not numbers of elements are arranged
increase consecutively. consecutively, in their increasing order,
So scientists had to leave gaps during the
arrangement of elements, to place So existence of new elements in-between
elements with similar chemical properties two adjacent elements is not probable.
in one group..
Differences between Mendeleev’s PT & Modern PT-
• Explanation of Modern Periodic Table:
When Elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic numbers, we
have-
a. The vertical columns, known as groups which are 18 in number.
b. The horizontal rows, known as periods which are 7 in number.
So, there are 18 groups and 7 periods in the modern periodic table.
2