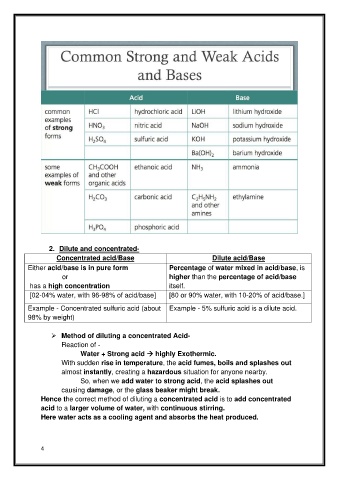
Page 4 - 3.LESSON NOTES (CH-2 CONCEPTS OF ACIDS & BASES)
P. 4
2. Dilute and concentrated-
Concentrated acid/Base Dilute acid/Base
Either acid/base is in pure form Percentage of water mixed in acid/base, is
or higher than the percentage of acid/base
has a high concentration itself.
[02-04% water, with 96-98% of acid/base] [80 or 90% water, with 10-20% of acid/base.]
Example - Concentrated sulfuric acid (about Example - 5% sulfuric acid is a dilute acid.
98% by weight)
➢ Method of diluting a concentrated Acid-
Reaction of -
Water + Strong acid → highly Exothermic.
With sudden rise in temperature, the acid fumes, boils and splashes out
almost instantly, creating a hazardous situation for anyone nearby.
So, when we add water to strong acid, the acid splashes out
causing damage, or the glass beaker might break.
Hence the correct method of diluting a concentrated acid is to add concentrated
acid to a larger volume of water, with continuous stirring.
Here water acts as a cooling agent and absorbs the heat produced.
4