Page 8 - LN
P. 8
CLASS AS A SYSTEM OF SOCIAL STRATIFICATION
Class system is different from the other forms of stratification in four main aspects.
1. The boundaries between class groups is not as clear cut as in the caste system.
2. Class status can be achieved and is not ascribed.
3. The class stratification is mainly based on inequalities with regard to possession of
economic resources.
4. The process of inequality operates through large scale impersonal association of the
members.
STATUS AND ROLE
Status: It is refers to the position an individual occupies in a group or in society. Each
status has certain defined rights and duties assigned to it. Examples of status- Doctor,
mother, teacher etc.
Status is of two types: Ascribed Status and Achieved Status
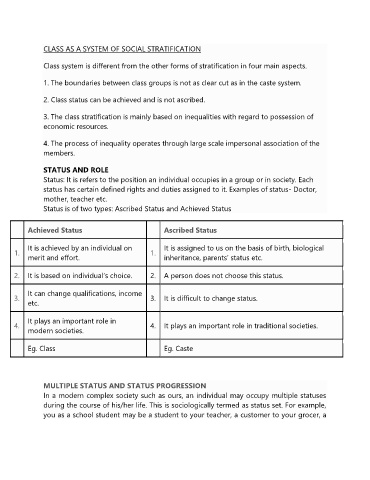
Achieved Status Ascribed Status
It is achieved by an individual on It is assigned to us on the basis of birth, biological
1. 1.
merit and effort. inheritance, parents‟ status etc.
2. It is based on individual‟s choice. 2. A person does not choose this status.
It can change qualifications, income
3. 3. It is difficult to change status.
etc.
It plays an important role in
4. 4. It plays an important role in traditional societies.
modern societies.
Eg. Class Eg. Caste
MULTIPLE STATUS AND STATUS PROGRESSION
In a modern complex society such as ours, an individual may occupy multiple statuses
during the course of his/her life. This is sociologically termed as status set. For example,
you as a school student may be a student to your teacher, a customer to your grocer, a