Page 4 - LN
P. 4
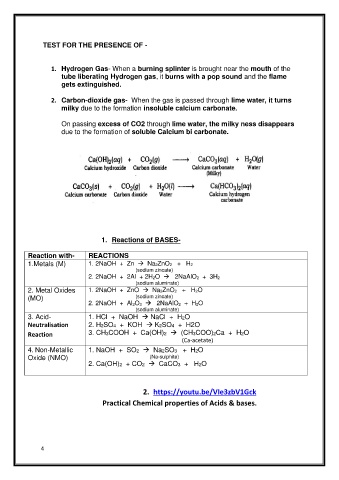
TEST FOR THE PRESENCE OF -
1. Hydrogen Gas- When a burning splinter is brought near the mouth of the
tube liberating Hydrogen gas, it burns with a pop sound and the flame
gets extinguished.
2. Carbon-dioxide gas- When the gas is passed through lime water, it turns
milky due to the formation insoluble calcium carbonate.
On passing excess of CO2 through lime water, the milky ness disappears
due to the formation of soluble Calcium bi carbonate.
1. Reactions of BASES-
Reaction with- REACTIONS
1.Metals (M) 1. 2NaOH + Zn → Na2ZnO2 + H2
(sodium zincate)
2. 2NaOH + 2Al + 2H2O → 2NaAlO2 + 3H2
(sodium aluminate)
2. Metal Oxides 1. 2NaOH + ZnO → Na2ZnO2 + H2O
(MO) (sodium zincate)
2. 2NaOH + Al2O3 → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
(sodium aluminate)
1
3. Acid- OH → NaCl + H2O
l + Na
.
HC
Neutralisation 2. H2SO4 + KOH → K2SO4 + H2O
3. CH3COOH + Ca(OH)2 → (CH3COO)2Ca + H2O
Reaction
(Ca-acetate)
4. Non-Metallic 1. NaOH + SO2 → Na2SO3 + H2O
Oxide (NMO) (Na-sulphite)
2. Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
2. https://youtu.be/VIe3zbV1Gck
Practical Chemical properties of Acids & bases.
4