Page 1 - CH - 2 - LN- 2.3
P. 1
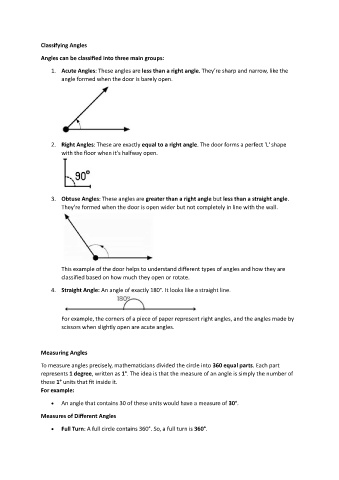
Classifying Angles
Angles can be classified into three main groups:
1. Acute Angles: These angles are less than a right angle. They’re sharp and narrow, like the
angle formed when the door is barely open.
2. Right Angles: These are exactly equal to a right angle. The door forms a perfect 'L' shape
with the floor when it’s halfway open.
3. Obtuse Angles: These angles are greater than a right angle but less than a straight angle.
They’re formed when the door is open wider but not completely in line with the wall.
This example of the door helps to understand different types of angles and how they are
classified based on how much they open or rotate.
4. Straight Angle: An angle of exactly 180°. It looks like a straight line.
For example, the corners of a piece of paper represent right angles, and the angles made by
scissors when slightly open are acute angles.
Measuring Angles
To measure angles precisely, mathematicians divided the circle into 360 equal parts. Each part
represents 1 degree, written as 1°. The idea is that the measure of an angle is simply the number of
these 1° units that fit inside it.
For example:
An angle that contains 30 of these units would have a measure of 30°.
Measures of Different Angles
Full Turn: A full circle contains 360°. So, a full turn is 360°.