Page 8 - CH - 2 - LN- 2.3
P. 8
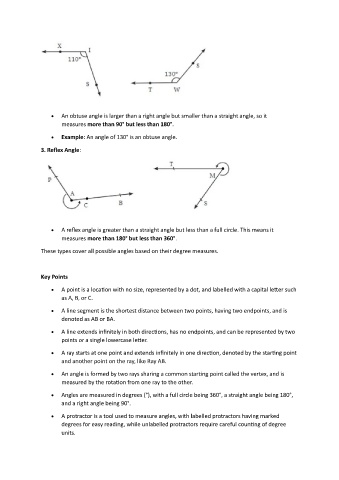
An obtuse angle is larger than a right angle but smaller than a straight angle, so it
measures more than 90° but less than 180°.
Example: An angle of 130° is an obtuse angle.
3. Reflex Angle:
A reflex angle is greater than a straight angle but less than a full circle. This means it
measures more than 180° but less than 360°.
These types cover all possible angles based on their degree measures.
Key Points
A point is a location with no size, represented by a dot, and labelled with a capital letter such
as A, B, or C.
A line segment is the shortest distance between two points, having two endpoints, and is
denoted as AB or BA.
A line extends infinitely in both directions, has no endpoints, and can be represented by two
points or a single lowercase letter.
A ray starts at one point and extends infinitely in one direction, denoted by the starting point
and another point on the ray, like Ray AB.
An angle is formed by two rays sharing a common starting point called the vertex, and is
measured by the rotation from one ray to the other.
Angles are measured in degrees (°), with a full circle being 360°, a straight angle being 180°,
and a right angle being 90°.
A protractor is a tool used to measure angles, with labelled protractors having marked
degrees for easy reading, while unlabelled protractors require careful counting of degree
units.