Page 4 - Microsoft Word - 4 Cell Membranes and transport.docx
P. 4
• the proteins provide hydrophilic areas that allow the • energy is used to make the channel/carrier proteins
molecules or ions to pass through the membrane change shape, transferring molecules/ions across the
which would otherwise be less permeable to them membrane in the process
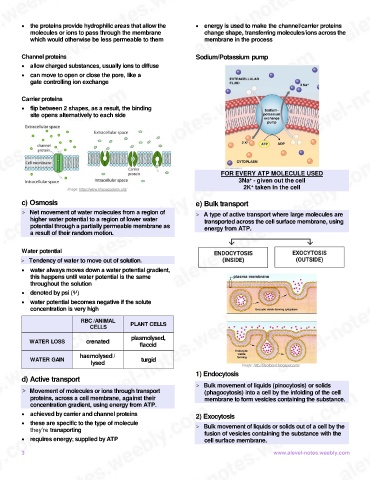
Channel proteins Sodium/Potassium pump
• allow charged substances, usually ions to diffuse
• can move to open or close the pore, like a
gate controlling ion exchange
Carrier proteins
• flip between 2 shapes, as a result, the binding
site opens alternatively to each side
FOR EVERY ATP MOLECULE USED
+
3Na - given out the cell
+
Image: https://www.khanacademy.org/ 2K taken in the cell
c) Osmosis e) Bulk transport
> Net movement of water molecules from a region of > A type of active transport where large molecules are
higher water potential to a region of lower water transported across the cell surface membrane, using
potential through a partially permeable membrane as energy from ATP.
a result of their random motion.
Water potential
> Tendency of water to move out of solution.
• water always moves down a water potential gradient,
this happens until water potential is the same
throughout the solution
• denoted by psi (Ѱ)
• water potential becomes negative if the solute
concentration is very high
RBC /ANIMAL PLANT CELLS
CELLS
plasmolysed,
WATER LOSS crenated flaccid
WATER GAIN haemolysed / turgid
lysed Image: http://lifeofplant.blogspot.com/
1) Endocytosis
d) Active transport
> Bulk movement of liquids (pinocytosis) or solids
> Movement of molecules or ions through transport (phagocytosis) into a cell by the infolding of the cell
proteins, across a cell membrane, against their membrane to form vesicles containing the substance.
concentration gradient, using energy from ATP.
• achieved by carrier and channel proteins 2) Exocytosis
• these are specific to the type of molecule > Bulk movement of liquids or solids out of a cell by the
they’re transporting
fusion of vesicles containing the substance with the
• requires energy; supplied by ATP cell surface membrane.
3 www.alevel-notes.weebly.com