Page 1 - CH6 (1)
P. 1
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
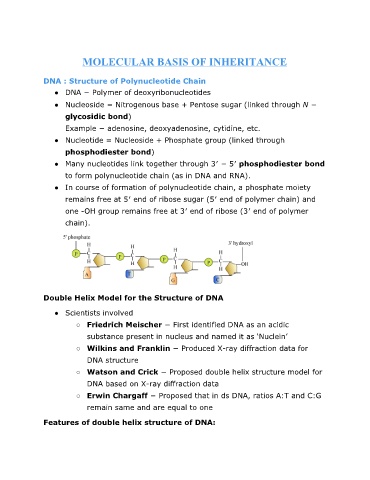
DNA : Structure of Polynucleotide Chain
● DNA − Polymer of deoxyribonucleotides
● Nucleoside = Nitrogenous base + Pentose sugar (linked throughN −
)
glycosidic bond
Example − adenosine, deoxyadenosine, cytidine, etc.
● Nucleotide = Nucleoside + Phosphate group (linked through
)
phosphodiester bond
5
′
p
● Many nucleotides link together through 3′ hosphodiester bond
−
to form polynucleotide chain (as in DNA and RNA).
● In course of formation of polynucleotide chain, a phosphate moiety
remains free at 5′ end of ribose sugar (5′ end of polymer chain) and
one OH group remains free at 3′ end of ribose (3′ end of polymer
chain).
Double Helix Model for the Structure of DNA
● Scientists involved
○ Friedrich Meischer− First identified DNA as an acidic
substance present in nucleus and named it as ‘Nuclein’
○ Wilkins and Franklin− Produced Xray diffraction data for
DNA structure
○ Watson and Crick− Proposed double helix structure model for
DNA based on Xray diffraction data
○ Erwin Chargaff− Proposed that in ds DNA, ratios A:T and C:G
remain same and are equal to one
Features of double helix structure of DNA: