Page 16 - Lesson Notes- Principle of inheritance & Variation
P. 16
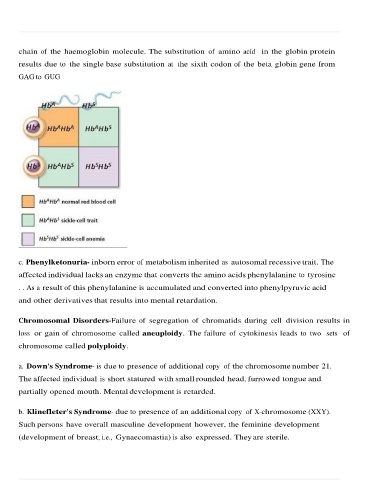
chain of the haemoglobin molecule. The substitution of amino acid in the globin protein
results due to the single base substitution at the sixth codon of the beta globin gene from
GAG to GUG
c. Phenylketonuria- inborn error of metabolism inherited as autosomal recessive trait. The
affected individual lacks an enzyme that converts the amino acids phenylalanine to tyrosine
. . As a result of this phenylalanine is accumulated and converted into phenylpyruvic acid
and other derivatives that results into mental retardation.
Chromosomal Disorders-Failure of segregation of chromatids during cell division results in
loss or gain of chromosome called aneuploidy. The failure of cytokinesis leads to two sets of
chromosome called polyploidy.
a. Down’s Syndrome- is due to presence of additional copy of the chromosome number 21.
The affected individual is short statured with small rounded head, furrowed tongue and
partially opened mouth. Mental development is retarded.
b. Klinefleter’s Syndrome- due to presence of an additional copy of X-chromosome (XXY).
Such persons have overall masculine development however, the feminine development
(development of breast, i.e., Gynaecomastia) is also expressed. They are sterile.
1616 /