Page 4 - LN-CH-16
P. 4
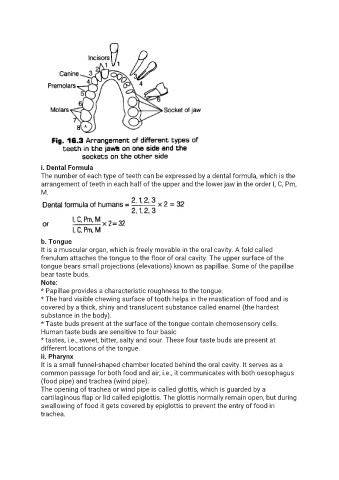
i. Dental Formula
The number of each type of teeth can be expressed by a dental formula, which is the
arrangement of teeth in each half of the upper and the lower jaw in the order I, C, Pm,
M.
b. Tongue
It is a muscular organ, which is freely movable in the oral cavity. A fold called
frenulum attaches the tongue to the floor of oral cavity. The upper surface of the
tongue bears small projections (elevations) known as papillae. Some of the papillae
bear taste buds.
Note:
* Papillae provides a characteristic roughness to the tongue.
* The hard visible chewing surface of tooth helps in the mastication of food and is
covered by a thick, shiny and translucent substance called enamel (the hardest
substance in the body).
* Taste buds present at the surface of the tongue contain chemosensory cells.
Human taste buds are sensitive to four basic
* tastes, i.e., sweet, bitter, salty and sour. These four taste buds are present at
different locations of the tongue.
ii. Pharynx
It is a small funnel-shaped chamber located behind the oral cavity. It serves as a
common passage for both food and air, i.e., it communicates with both oesophagus
(food pipe) and trachea (wind pipe).
The opening of trachea or wind pipe is called glottis, which is guarded by a
cartilaginous flap or lid called epiglottis. The glottis normally remain open, but during
swallowing of food it gets covered by epiglottis to prevent the entry of food in
trachea.