Page 5 - Lesson notes- Plant Respiration
P. 5
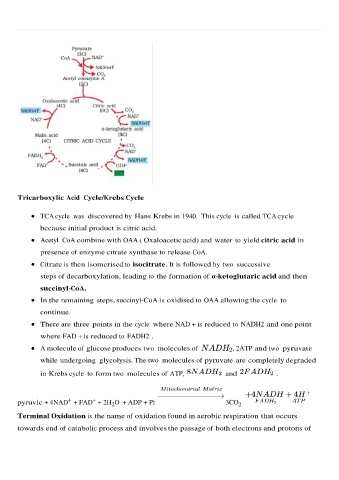
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle/Krebs Cycle
TCA cycle was discovered by Hans Krebs in 1940. This cycle is called TCA cycle
because initial product is citric acid.
Acetyl CoA combine with OAA ( Oxaloacetic acid) and water to yield citric acid in
presence of enzyme citrate synthase to release CoA.
Citrate is then isomerised to isocitrate. It is followed by two successive
steps of decarboxylation, leading to the formation of α-ketoglutaric acid and then
succinyl-CoA.
In the remaining steps, succinyl-CoA is oxidised to OAA allowing the cycle to
continue.
There are three points in the cycle where NAD + is reduced to NADH2 and one point
where FAD + is reduced to FADH2 .
A molecule of glucose produces two molecules of , 2ATP and two pyruvate
while undergoing glycolysis. The two molecules of pyruvate are completely degraded
in Krebs cycle to form two molecules of ATP, and .
+
+
pyruvic + 4NAD + FAD + 2H O + ADP + Pi 3CO 2
2
Terminal Oxidation is the name of oxidation found in aerobic respiration that occurs
towards end of catabolic process and involves the passage of both electrons and protons of