Page 4 - Lesson notes- Plant Respiration
P. 4
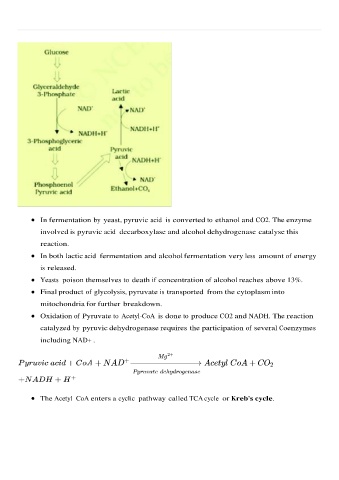
In fermentation by yeast, pyruvic acid is converted to ethanol and CO2. The enzyme
involved is pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase catalyse this
reaction.
In both lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation very less amount of energy
is released.
Yeasts poison themselves to death if concentration of alcohol reaches above 13%.
Final product of glycolysis, pyruvate is transported from the cytoplasm into
mitochondria for further breakdown.
Oxidation of Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA is done to produce CO2 and NADH. The reaction
catalyzed by pyruvic dehydrogenase requires the participation of several Coenzymes
including NAD+ .
The Acetyl CoA enters a cyclic pathway called TCA cycle or Kreb’s cycle.