Page 8 - LN-PHOTOSYNTHESIS IN PLANTS
P. 8
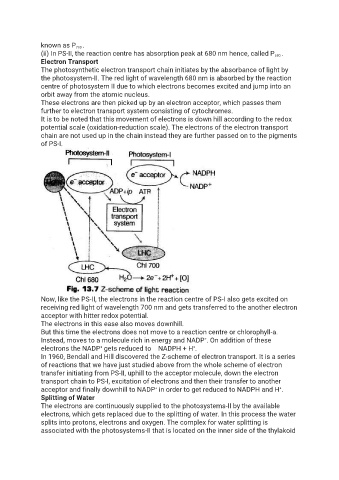
known as P 700 .
(ii) In PS-II, the reaction centre has absorption peak at 680 nm hence, called P 680 .
Electron Transport
The photosynthetic electron transport chain initiates by the absorbance of light by
the photosystem-II. The red light of wavelength 680 nm is absorbed by the reaction
centre of photosystem II due to which electrons becomes excited and jump into an
orbit away from the atomic nucleus.
These electrons are then picked up by an electron acceptor, which passes them
further to electron transport system consisting of cytochromes.
It is to be noted that this movement of electrons is down hill according to the redox
potential scale (oxidation-reduction scale). The electrons of the electron transport
chain are not used up in the chain instead they are further passed on to the pigments
of PS-I.
Now, like the PS-II, the electrons in the reaction centre of PS-I also gets excited on
receiving red light of wavelength 700 nm and gets transferred to the another electron
acceptor with hitter redox potential.
The electrons in this ease also moves downhill.
But this time the electrons does not move to a reaction centre or chlorophyll-a.
Instead, moves to a molecule rich in energy and NADP . On addition of these
+
electrons the NADP gets reduced to NADPH + H .
+
+
In 1960, Bendall and Hill discovered the Z-scheme of electron transport. It is a series
of reactions that we have just studied above from the whole scheme of electron
transfer initiating from PS-II, uphill to the acceptor molecule, down the electron
transport chain to PS-I, excitation of electrons and then their transfer to another
acceptor and finally downhill to NADP in order to get reduced to NADPH and H .
+
+
Splitting of Water
The electrons are continuously supplied to the photosystems-II by the available
electrons, which gets replaced due to the splitting of water. In this process the water
splits into protons, electrons and oxygen. The complex for water splitting is
associated with the photosystems-II that is located on the inner side of the thylakoid