Page 12 - LN-PHOTOSYNTHESIS IN PLANTS
P. 12
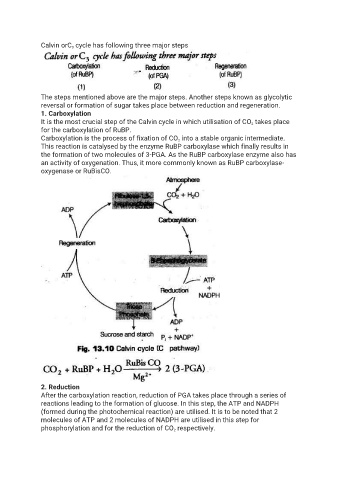
Calvin orC 3 cycle has following three major steps
The steps mentioned above are the major steps. Another steps known as glycolytic
reversal or formation of sugar takes place between reduction and regeneration.
1. Carboxylation
It is the most crucial step of the Calvin cycle in which utilisation of CO 2 takes place
for the carboxylation of RuBP.
Carboxylation is the process of fixation of CO 2 into a stable organic intermediate.
This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme RuBP carboxylase which finally results in
the formation of two molecules of 3-PGA. As the RuBP carboxylase enzyme also has
an activity of oxygenation. Thus, it more commonly known as RuBP carboxylase-
oxygenase or RuBisCO.
2. Reduction
After the carboxylation reaction, reduction of PGA takes place through a series of
reactions leading to the formation of glucose. In this step, the ATP and NADPH
(formed during the photochemical reaction) are utilised. It is to be noted that 2
molecules of ATP and 2 molecules of NADPH are utilised in this step for
phosphorylation and for the reduction of CO 2 respectively.