Page 12 - LN-ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANT
P. 12
arrangement of xylem and phloem is the characteristic to particular plant organs.
However, a few exception are also there.
On the basis of arrangement of xylem and phloem in the vascular bundles, there are
three types of bundles, i.e., radial, conjoint and concentric.
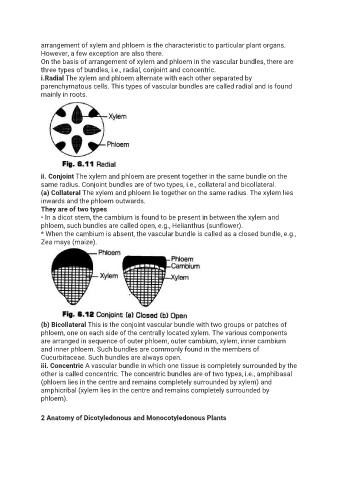
i.Radial The xylem and phloem alternate with each other separated by
parenchymatous cells. This types of vascular bundles are called radial and is found
mainly in roots.
ii. Conjoint The xylem and phloem are present together in the same bundle on the
same radius. Conjoint bundles are of two types, i.e., collateral and bicollateral.
(a) Collateral The xylem and phloem lie together on the same radius. The xylem lies
inwards and the phloem outwards.
They are of two types
• In a dicot stem, the cambium is found to be present in between the xylem and
phloem, such bundles are called open, e.g., Helianthus (sunflower).
* When the cambium is absent, the vascular bundle is called as a closed bundle, e.g.,
Zea mays (maize).
(b) Bicollateral This is the conjoint vascular bundle with two groups or patches of
phloem, one on each side of the centrally located xylem. The various components
are arranged in sequence of outer phloem, outer cambium, xylem, inner cambium
and inner phloem. Such bundles are commonly found in the members of
Cucurbitaceae. Such bundles are always open.
iii. Concentric A vascular bundle in which one tissue is completely surrounded by the
other is called concentric. The concentric bundles are of two types, i.e., amphibasal
(phloem lies in the centre and remains completely surrounded by xylem) and
amphicribal (xylem lies in the centre and remains completely surrounded by
phloem).
2 Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants