Page 1 - LN
P. 1
SAI International School
Class-IX
Subject- Chemistry
Topic-Atoms and Molecules
Topic-Ions (positive ion and negative ion), calculations of valency of
ions
LESSON NOTE
Ions
The charged particles (atoms) are called ions, they charge or negative charge on it:
-
Negatively charged ion is called anion (Cl )
+
Positively charge ion is called cation (Na ).
Polyatomic ions: These are the ions which contain atoms of more than one element
which carry a single charge and behave as a single unit in chemical combinations.
+
2-
Example: NH 4 ,SO 4
• Valency
The combining capacity of an element is known as its valency: Valency is used to
find out how atom of an element will combine with the atom of another element to form
a chemical compound.
(Every atom want, to become stable, to do so it may lose, gain or share electrons.
(i) If an atom consists of 1, 2 or 3 electrons in its valance shell then its valency is 1,
2 or 3 respectively,
(ii) If an atom consists of 5, 6 or 7 electrons in the outermost shell, then it will gain 3,
2 or 1 electron respectively and its valency will be 3, 2 or 1 respectively.
(ii) If an atom has 4 electrons in the outermost shell than it will she this electron and
hence its valency will be 4.
(iv) If an atom has 8 electrons in the outermost shell then its valency is 0.
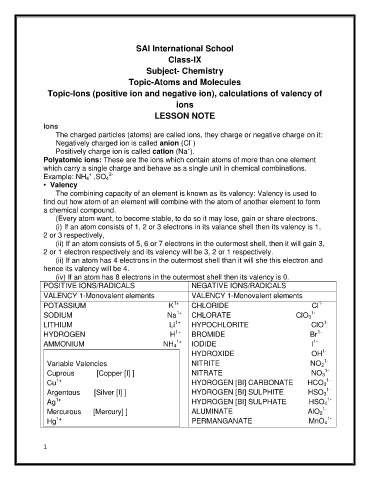
POSITIVE IONS/RADICALS NEGATIVE IONS/RADICALS
VALENCY 1-Monovalent elements VALENCY 1-Monovalent elements
1+
1-
L
CH
POTASSIUM K Cl
ORIDE
1+
1-
ORA
L
SODIUM Na ClO 3
E
T
CH
1+
1-
E
OCHLO
RIT
LITHIUM Li ClO
P
HY
1+
1-
HYDROGEN H Br
IDE
ROM
B
1+
1-
AMMONIUM NH 4 IODIDE I
1-
HYDROXIDE OH
1-
Variable Valencies NITRITE NO 2
1-
Cuprous [Copper [I] ] NITRATE NO 3
1-
1+
Cu HYDROGEN [BI] CARBONATE HCO 3
1-
Argentous [Silver [I] ] HYDROGEN [BI] SULPHITE HSO 3
1-
1+
Ag HYDROGEN [BI] SULPHATE HSO 4
1-
Mercurous [Mercury] ] ALUMINATE AlO 2
1+
Hg PERMANGANATE MnO 4 1-
1