Page 6 - LN
P. 6
The immune system recruits the disease-causing microbes and destroys them.
This is known as inflammation. The severity of disease manifestations depends
upon the number of microbes in the body.
The immune system keeps a check on the number of microbes in the body.
When the immune system is damaged due to a deadly virus like HIV, the body
can no longer fight the infections and the patient does not survive for long.
Inflammation is the immune system's response to harmful stimuli, such as
pathogens, damaged cells, toxic compounds, or irradiation, and acts by removing
injurious stimuli and initiating the healing process. Inflammation is therefore a
defense mechanism that is vital to health.
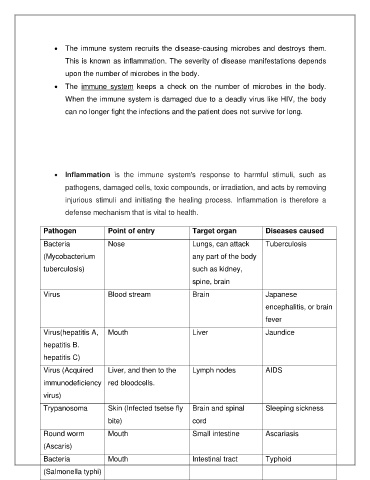
Pathogen Point of entry Target organ Diseases caused
Bacteria Nose Lungs, can attack Tuberculosis
(Mycobacterium any part of the body
tuberculosis) such as kidney,
spine, brain
Virus Blood stream Brain Japanese
encephalitis, or brain
fever
Virus(hepatitis A, Mouth Liver Jaundice
hepatitis B.
hepatitis C)
Virus (Acquired Liver, and then to the Lymph nodes AIDS
immunodeficiency red bloodcells.
virus)
Trypanosoma Skin (Infected tsetse fly Brain and spinal Sleeping sickness
bite) cord
Round worm Mouth Small intestine Ascariasis
(Ascaris)
Bacteria Mouth Intestinal tract Typhoid
(Salmonella typhi)