Page 2 - LN
P. 2
(A) Cattle Farming / Husbandry
Cattle farming / Husbandry is done for two purposes:
1. Dairy: for getting milk.
2. Draught: animals are used for agricultural tasks like tilling, irrigation and carting.
On the above basis, the cattle are divided into two categories:
Milch breeds (dairy animals): These include the animals which are kept for
obtaining milk. Indian milch cattle belong to two different species- Cows (Bos
indicus) and Buffaloes (Bos bubalis).
Draught animals: These animals are used in agriculture and transportation.
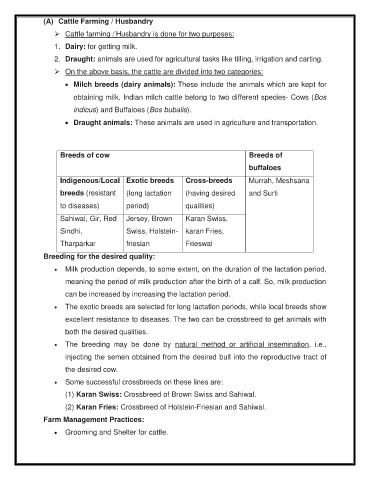
Breeds of cow Breeds of
buffaloes
Indigenous/Local Exotic breeds Cross-breeds Murrah, Meshsana
breeds (resistant (long lactation (having desired and Surti
to diseases) period) qualities)
Sahiwal, Gir, Red Jersey, Brown Karan Swiss,
Sindhi, Swiss, Holstein- karan Fries,
Tharparkar friesian Frieswal
Breeding for the desired quality:
Milk production depends, to some extent, on the duration of the lactation period,
meaning the period of milk production after the birth of a calf. So, milk production
can be increased by increasing the lactation period.
The exotic breeds are selected for long lactation periods, while local breeds show
excellent resistance to diseases. The two can be crossbreed to get animals with
both the desired qualities.
The breeding may be done by natural method or artificial insemination, i.e.,
injecting the semen obtained from the desired bull into the reproductive tract of
the desired cow.
Some successful crossbreeds on these lines are:
(1) Karan Swiss: Crossbreed of Brown Swiss and Sahiwal.
(2) Karan Fries: Crossbreed of Holstein-Friesian and Sahiwal.
Farm Management Practices:
Grooming and Shelter for cattle.