Page 2 - Lesson Notes
P. 2
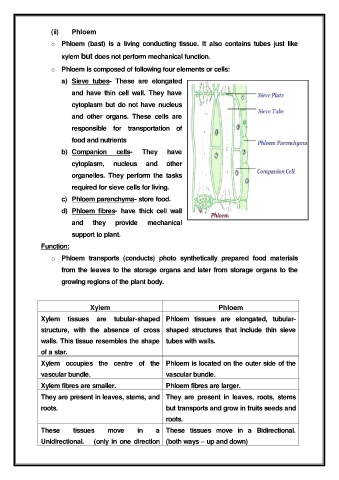
(ii) Phloem
o Phloem (bast) is a living conducting tissue. It also contains tubes just like
xylem but does not perform mechanical function.
o Phloem is composed of following four elements or cells:
a) Sieve tubes- These are elongated
and have thin cell wall. They have
cytoplasm but do not have nucleus
and other organs. These cells are
responsible for transportation of
food and nutrients
b) Companion cells- They have
cytoplasm, nucleus and other
organelles. They perform the tasks
required for sieve cells for living.
c) Phloem parenchyma- store food.
d) Phloem fibres- have thick cell wall
and they provide mechanical
support to plant.
Function:
o Phloem transports (conducts) photo synthetically prepared food materials
from the leaves to the storage organs and later from storage organs to the
growing regions of the plant body.
Xylem Phloem
Xylem tissues are tubular-shaped Phloem tissues are elongated, tubular-
structure, with the absence of cross shaped structures that include thin sieve
walls. This tissue resembles the shape tubes with walls.
of a star.
Xylem occupies the centre of the Phloem is located on the outer side of the
vascular bundle. vascular bundle.
Xylem fibres are smaller. Phloem fibres are larger.
They are present in leaves, stems, and They are present in leaves, roots, stems
roots. but transports and grow in fruits seeds and
roots.
These tissues move in a These tissues move in a Bidirectional.
Unidirectional. (only in one direction (both ways – up and down)