Page 2 - ln1
P. 2
Applications of Pythagoras Theorem:
To know if the triangle is a right-angled triangle or not.
In a right-angled triangle, we can calculate the length of any side if the other two sides
are given.
To find the diagonal of a square.
Example:
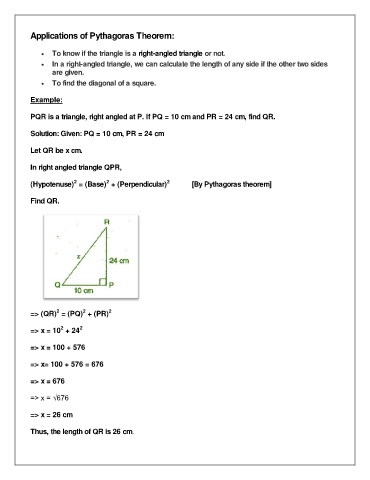
PQR is a triangle, right angled at P. If PQ = 10 cm and PR = 24 cm, find QR.
Solution: Given: PQ = 10 cm, PR = 24 cm
Let QR be x cm.
In right angled triangle QPR,
2
2
2
(Hypotenuse) = (Base) + (Perpendicular) [By Pythagoras theorem]
Find QR.
2
2
2
=> (QR) = (PQ) + (PR)
2
2
=> x = 10 + 24
=> x = 100 + 576
=> x= 100 + 576 = 676
=> x = 676
=> x = √676
=> x = 26 cm
Thus, the length of QR is 26 cm.