Page 4 - ln1
P. 4
In this process, sugar (glucose) breaks down into carbon dioxide and alcohol
with the production of energy.
Alcohol and carbon dioxide are formed at the end of anaerobic respiration.
The amount of energy released is much less as compared to aerobic
respiration.
Several bacteria and fungi, such as, yeast can respire anaerobically.
Yeast is also used in wine and beer industries.
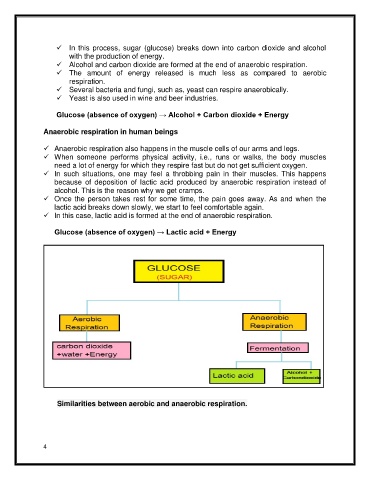
Glucose (absence of oxygen) → Alcohol + Carbon dioxide + Energy
Anaerobic respiration in human beings
Anaerobic respiration also happens in the muscle cells of our arms and legs.
When someone performs physical activity, i.e., runs or walks, the body muscles
need a lot of energy for which they respire fast but do not get sufficient oxygen.
In such situations, one may feel a throbbing pain in their muscles. This happens
because of deposition of lactic acid produced by anaerobic respiration instead of
alcohol. This is the reason why we get cramps.
Once the person takes rest for some time, the pain goes away. As and when the
lactic acid breaks down slowly, we start to feel comfortable again.
In this case, lactic acid is formed at the end of anaerobic respiration.
Glucose (absence of oxygen) → Lactic acid + Energy
Similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
4