Page 2 - LN 6
P. 2
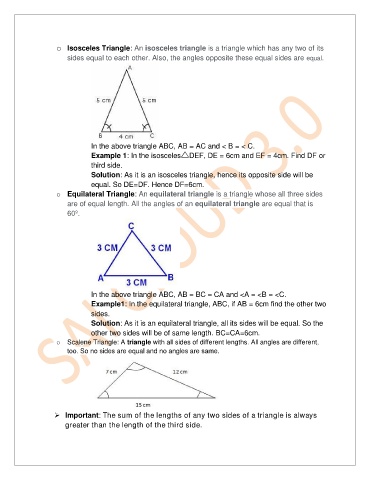
o Isosceles Triangle: An isosceles triangle is a triangle which has any two of its
sides equal to each other. Also, the angles opposite these equal sides are equal.
In the above triangle ABC, AB = AC and < B = < C.
Example 1: In the isosceles DEF, DE = 6cm and EF = 4cm. Find DF or
third side.
Solution: As it is an isosceles triangle, hence its opposite side will be
equal. So DE=DF. Hence DF=6cm.
o Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle is a triangle whose all three sides
are of equal length. All the angles of an equilateral triangle are equal that is
60º.
In the above triangle ABC, AB = BC = CA and <A = <B = <C.
Example1: In the equilateral triangle, ABC, if AB = 6cm find the other two
sides.
Solution: As it is an equilateral triangle, all its sides will be equal. So the
other two sides will be of same length. BC=CA=6cm.
o Scalene Triangle: A triangle with all sides of different lengths. All angles are different,
too. So no sides are equal and no angles are same.
Important: The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always
greater than the length of the third side.