Page 2 - Lesson note 4
P. 2
(ii) Lyophobic colloids (lyo- means solvent and phobia means
hating)
The colloidal solution in which the dispersed phase has less affinity towards
dispersion medium is called lyophobic colloid.
Example-colloidal solutions of metals and their sulphides.
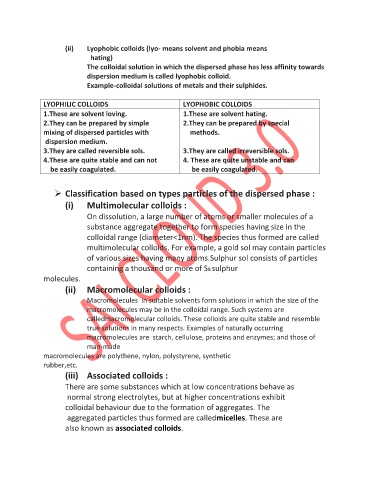
LYOPHILIC COLLOIDS LYOPHOBIC COLLOIDS
1.These are solvent loving. 1.These are solvent hating.
2.They can be prepared by simple 2.They can be prepared by special
mixing of dispersed particles with methods.
dispersion medium.
3.They are called reversible sols. 3.They are called irreversible sols.
4.These are quite stable and can not 4. These are quite unstable and can
be easily coagulated. be easily coagulated.
Classification based on types particles of the dispersed phase :
(i) Multimolecular colloids :
On dissolution, a large number of atoms or smaller molecules of a
substance aggregate together to form species having size in the
colloidal range (diameter<1nm). The species thus formed are called
multimolecular colloids. For example, a gold sol may contain particles
of various sizes having many atoms.Sulphur sol consists of particles
containing a thousand or more of S8 sulphur
molecules.
(ii) Macromolecular colloids :
Macromolecules in suitable solvents form solutions in which the size of the
macromolecules may be in the colloidal range. Such systems are
calledmacromolecular colloids. These colloids are quite stable and resemble
true solutions in many respects. Examples of naturally occurring
macromolecules are starch, cellulose, proteins and enzymes; and those of
man-made
macromolecules are polythene, nylon, polystyrene, synthetic
rubber,etc.
(iii) Associated colloids :
There are some substances which at low concentrations behave as
normal strong electrolytes, but at higher concentrations exhibit
colloidal behaviour due to the formation of aggregates. The
aggregated particles thus formed are calledmicelles. These are
also known as associated colloids.