Page 4 - LN2
P. 4
Domain names are used in URLs to identify particular Web pages. For example, in the URL
http://www.pcwebopedia.com/index.html, the domain name is pcwebopedia.com.
Every domain name has a suffix that indicates which top level domain (TLD) it belongs to. There are only
a limited number of such domains. For example:
gov - Government agencies
edu - Educational institutions
org - Organizations (nonprofit)
mil - Military
com - commercial business
net - Network organizations
ca - Canada
th - Thailand
in - India
Because the Internet is based on IP addresses, not domain names, every Web server requires a Domain
Name System (DNS) server to translate domain names into IP addresses.
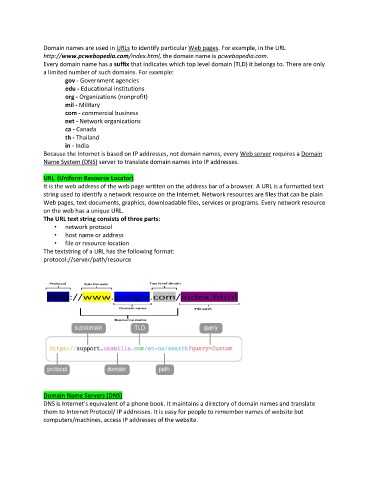
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
It is the web address of the web page written on the address bar of a browser. A URL is a formatted text
string used to identify a network resource on the Internet. Network resources are files that can be plain
Web pages, text documents, graphics, downloadable files, services or programs. Every network resource
on the web has a unique URL.
The URL text string consists of three parts:
• network protocol
• host name or address
• file or resource location
The textstring of a URL has the following format:
protocol://server/path/resource
Domain Name Servers (DNS)
DNS is Internet's equivalent of a phone book. It maintains a directory of domain names and translate
them to Internet Protocol/ IP addresses. It is easy for people to remember names of website but
computers/machines, access IP addresses of the website.