Page 2 - Lesson Note 7
P. 2
Complementary Goods- It refers to those goods which are used together to satisfy a
particular want. Demand for a given commodity varies inversely with the price of a
complementary good. For ex- car and petrol
Change in price of Complementary Good- An increase productivity decrease in the price
of complementary goods inversely affect the demand for the given good.
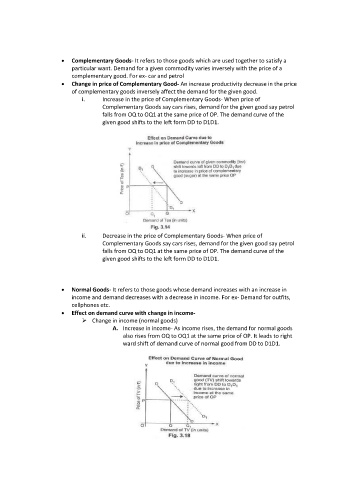
i. Increase in the price of Complementary Goods- When price of
Complementary Goods say cars rises, demand for the given good say petrol
falls from OQ to OQ1 at the same price of OP. The demand curve of the
given good shifts to the left form DD to D1D1.
ii. Decrease in the price of Complementary Goods- When price of
Complementary Goods say cars rises, demand for the given good say petrol
falls from OQ to OQ1 at the same price of OP. The demand curve of the
given good shifts to the left form DD to D1D1.
Normal Goods- It refers to those goods whose demand increases with an increase in
income and demand decreases with a decrease in income. For ex- Demand for outfits,
cellphones etc.
Effect on demand curve with change in income-
Change in income (normal goods)
A. Increase in income- As income rises, the demand for normal goods
also rises from OQ to OQ1 at the same price of OP. It leads to right
ward shift of demand curve of normal good from DD to D1D1.