Page 4 - HA
P. 4
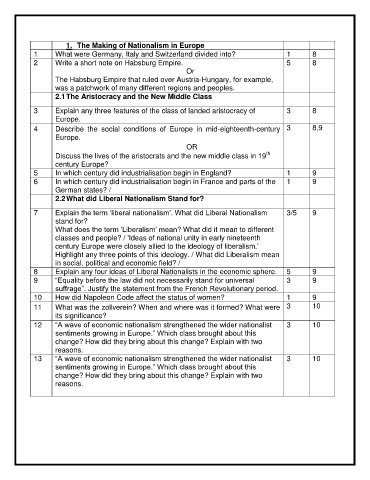
1. The Making of Nationalism in Europe
1 What were Germany, Italy and Switzerland divided into? 1 8
2 Write a short note on Habsburg Empire. 5 8
Or
The Habsburg Empire that ruled over Austria-Hungary, for example,
was a patchwork of many different regions and peoples.
2.1 The Aristocracy and the New Middle Class
3 Explain any three features of the class of landed aristocracy of 3 8
Europe.
4 Describe the social conditions of Europe in mid-eighteenth-century 3 8,9
Europe.
OR
th
Discuss the lives of the aristocrats and the new middle class in 19
century Europe?
5 In which century did industrialisation begin in England? 1 9
6 In which century did industrialisation begin in France and parts of the 1 9
German states? /
2.2 What did Liberal Nationalism Stand for?
7 Explain the term „liberal nationalism‟. What did Liberal Nationalism 3/5 9
stand for?
What does the term „Liberalism‟ mean? What did it mean to different
classes and people? / 'Ideas of national unity in early nineteenth
century Europe were closely allied to the ideology of liberalism.'
Highlight any three points of this ideology. / What did Liberalism mean
in social, political and economic field? /
8 Explain any four ideas of Liberal Nationalists in the economic sphere. 5 9
9 “Equality before the law did not necessarily stand for universal 3 9
suffrage”. Justify the statement from the French Revolutionary period.
10 How did Napoleon Code affect the status of women? 1 9
11 What was the zollverein? When and where was it formed? What were 3 10
its significance?
12 “A wave of economic nationalism strengthened the wider nationalist 3 10
sentiments growing in Europe.” Which class brought about this
change? How did they bring about this change? Explain with two
reasons.
13 “A wave of economic nationalism strengthened the wider nationalist 3 10
sentiments growing in Europe.” Which class brought about this
change? How did they bring about this change? Explain with two
reasons.