Page 3 - LN
P. 3
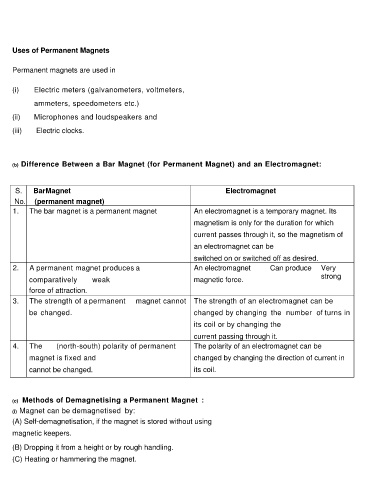
Uses of Permanent Magnets
Permanent magnets are used in
(i) Electric meters (galvanometers, voltmeters,
ammeters, speedometers etc.)
(ii) Microphones and loudspeakers and
(iii) Electric clocks.
(b) Difference Between a Bar Magnet (for Permanent Magnet) and an Electromagnet:
S. BarMagnet Electromagnet
No. (permanent magnet)
1. The bar magnet is a permanent magnet a An electromagnet is a temporary magnet. Its
magnetism is only for the duration for which
current passes through it, so the magnetism of
an electromagnet can be
switched on or switched off as desired.
2. A permanent magnet produces a An electromagnet Can produce Very
strong
comparatively weak magnetic force.
force of attraction.
3. The strength of a permanent magnet cannot The strength of an electromagnet can be
be changed. changed by changing the number of turns in
its coil or by changing the
current passing through it.
4. The (north-south) polarity of permanent The polarity of an electromagnet can be
magnet is fixed and changed by changing the direction of current in
cannot be changed. its coil.
(c) Methods of Demagnetising a Permanent Magnet :
(i) Magnet can be demagnetised by:
(A) Self-demagnetisation, if the magnet is stored without using
magnetic keepers.
(B) Dropping it from a height or by rough handling.
(C) Heating or hammering the magnet.