Page 3 - 2. Lesson note - Ch-3 Concept mapping
P. 3
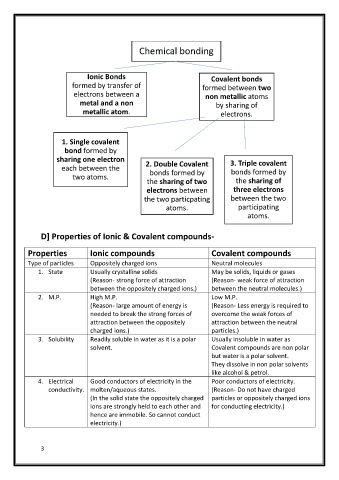
Chemical bonding
Ionic Bonds Covalent bonds
formed by transfer of formed between two
electrons between a non metallic atoms
metal and a non by sharing of
metallic atom. electrons.
1. Single covalent
bond formed by
sharing one electron 3. Triple covalent
each between the 2. Double Covalent bonds formed by
bonds formed by
two atoms.
the sharing of two the sharing of
electrons between three electrons
the two particpating between the two
atoms. participating
atoms.
D] Properties of Ionic & Covalent compounds-
Properties Ionic compounds Covalent compounds
Type of particles Oppositely charged ions Neutral molecules
1. State Usually crystalline solids May be solids, liquids or gases
(Reason- strong force of attraction (Reason- weak force of attraction
between the oppositely charged ions.) between the neutral molecules.)
Low
2. M.P. High M.P. M.P.
(Reason- large amount of energy is (Reason- Less energy is required to
needed to break the strong forces of overcome the weak forces of
attraction between the oppositely attraction between the neutral
charged ions.) particles.)
3. Solubility Readily soluble in water as it is a polar Usually insoluble in water as
solvent. Covalent compounds are non polar
but water is a polar solvent.
They dissolve in non polar solvents
like alcohol & petrol.
4. Electrical Good conductors of electricity in the Poor conductors of electricity.
conductivity. molten/aqueous states. (Reason- Do not have charged
(In the solid state the oppositely charged particles or oppositely charged ions
ions are strongly held to each other and for conducting electricity.)
hence are immobile. So cannot conduct
electricity.)
3