Page 5 - LN
P. 5
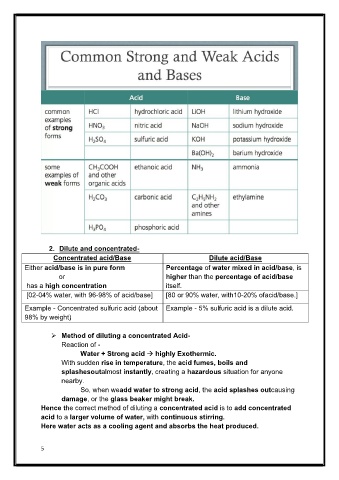
2. Dilute and concentrated-
Concentrated acid/Base Dilute acid/Base
Either acid/base is in pure form Percentage of water mixed in acid/base, is
or higher than the percentage of acid/base
has a high concentration itself.
[02-04% water, with 96-98% of acid/base] [80 or 90% water, with10-20% ofacid/base.]
Example - Concentrated sulfuric acid (about Example - 5% sulfuric acid is a dilute acid.
98% by weight)
Method of diluting a concentrated Acid-
Reaction of -
Water + Strong acid highly Exothermic.
With sudden rise in temperature, the acid fumes, boils and
splashesoutalmost instantly, creating a hazardous situation for anyone
nearby.
So, when weadd water to strong acid, the acid splashes outcausing
damage, or the glass beaker might break.
Hence the correct method of diluting a concentrated acid is to add concentrated
acid to a larger volume of water, with continuous stirring.
Here water acts as a cooling agent and absorbs the heat produced.
5