Page 2 - LN
P. 2
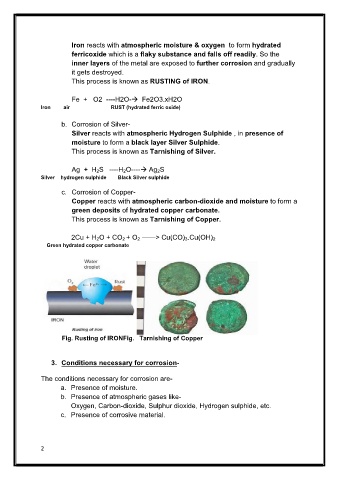
Iron reacts with atmospheric moisture & oxygen to form hydrated
ferricoxide which is a flaky substance and falls off readily. So the
inner layers of the metal are exposed to further corrosion and gradually
it gets destroyed.
This process is known as RUSTING of IRON.
Fe + O2 ----H2O- Fe2O3.xH2O
Iron air RUST (hydrated ferric oxide)
b. Corrosion of Silver-
Silver reacts with atmospheric Hydrogen Sulphide , in presence of
moisture to form a black layer Silver Sulphide.
This process is known as Tarnishing of Silver.
Ag + H 2S ----H 2O---- Ag 2S
Silver hydrogen sulphide Black Silver sulphide
c. Corrosion of Copper-
Copper reacts with atmospheric carbon-dioxide and moisture to form a
green deposits of hydrated copper carbonate.
This process is known as Tarnishing of Copper.
2Cu + H 2O + CO 2 + O 2 ——> Cu(CO) 3.Cu(OH) 2
Green hydrated copper carbonate
Fig. Rusting of IRONFig. Tarnishing of Copper
3. Conditions necessary for corrosion-
The conditions necessary for corrosion are-
a. Presence of moisture.
b. Presence of atmospheric gases like-
Oxygen, Carbon-dioxide, Sulphur dioxide, Hydrogen sulphide, etc.
c. Presence of corrosive material.
2