Page 3 - 2.4-Lesson Notes-Coordination in Plants-(i)
P. 3
Plant movement
Movement in plants due to external stimuli are of two types: tropic and nastic
movements.
Tropisms
• When the direction of external stimulus decides the direction of response in
the form of growth it is called tropism.
• Directional growth movement of a plant part.
• It can be in the direction of the stimulus or away from the stimulus.
• If the growth of a plant is in the direction of stimulus, it is called positive
tropism.
• If the growth of a plant is in the opposite direction or away from that of a
stimulus, it is called negative stimulus.
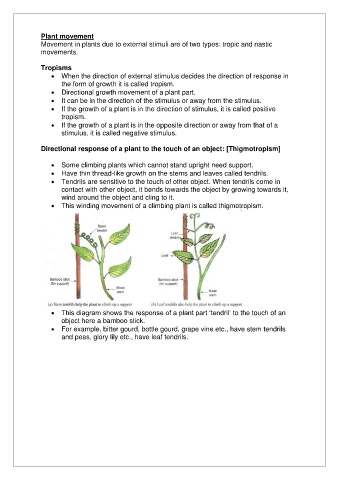
Directional response of a plant to the touch of an object: [Thigmotropism]
• Some climbing plants which cannot stand upright need support.
• Have thin thread-like growth on the stems and leaves called tendrils.
• Tendrils are sensitive to the touch of other object. When tendrils come in
contact with other object, it bends towards the object by growing towards it,
wind around the object and cling to it.
• This winding movement of a climbing plant is called thigmotropism.
• This diagram shows the response of a plant part ‘tendril’ to the touch of an
object here a bamboo stick.
• For example, bitter gourd, bottle gourd, grape vine etc., have stem tendrils
and peas, glory lily etc., have leaf tendrils.