Page 3 - CBW Light Shadows & Reflections
P. 3
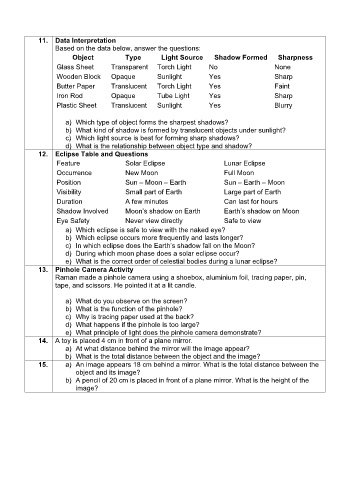
11. Data Interpretation
Based on the data below, answer the questions:
Object Type Light Source Shadow Formed Sharpness
Glass Sheet Transparent Torch Light No None
Wooden Block Opaque Sunlight Yes Sharp
Butter Paper Translucent Torch Light Yes Faint
Iron Rod Opaque Tube Light Yes Sharp
Plastic Sheet Translucent Sunlight Yes Blurry
a) Which type of object forms the sharpest shadows?
b) What kind of shadow is formed by translucent objects under sunlight?
c) Which light source is best for forming sharp shadows?
d) What is the relationship between object type and shadow?
12. Eclipse Table and Questions
Feature Solar Eclipse Lunar Eclipse
Occurrence New Moon Full Moon
Position Sun – Moon – Earth Sun – Earth – Moon
Visibility Small part of Earth Large part of Earth
Duration A few minutes Can last for hours
Shadow Involved Moon’s shadow on Earth Earth’s shadow on Moon
Eye Safety Never view directly Safe to view
a) Which eclipse is safe to view with the naked eye?
b) Which eclipse occurs more frequently and lasts longer?
c) In which eclipse does the Earth’s shadow fall on the Moon?
d) During which moon phase does a solar eclipse occur?
e) What is the correct order of celestial bodies during a lunar eclipse?
13. Pinhole Camera Activity
Raman made a pinhole camera using a shoebox, aluminium foil, tracing paper, pin,
tape, and scissors. He pointed it at a lit candle.
a) What do you observe on the screen?
b) What is the function of the pinhole?
c) Why is tracing paper used at the back?
d) What happens if the pinhole is too large?
e) What principle of light does the pinhole camera demonstrate?
14. A toy is placed 4 cm in front of a plane mirror.
a) At what distance behind the mirror will the image appear?
b) What is the total distance between the object and the image?
15. a) An image appears 18 cm behind a mirror. What is the total distance between the
object and its image?
b) A pencil of 20 cm is placed in front of a plane mirror. What is the height of the
image?