Page 6 - CH - 2 - LN - 2.4
P. 6
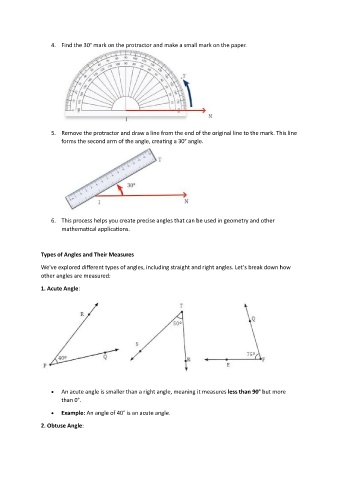
4. Find the 30° mark on the protractor and make a small mark on the paper.
5. Remove the protractor and draw a line from the end of the original line to the mark. This line
forms the second arm of the angle, creating a 30° angle.
6. This process helps you create precise angles that can be used in geometry and other
mathematical applications.
Types of Angles and Their Measures
We've explored different types of angles, including straight and right angles. Let’s break down how
other angles are measured:
1. Acute Angle:
An acute angle is smaller than a right angle, meaning it measures less than 90° but more
than 0°.
Example: An angle of 40° is an acute angle.
2. Obtuse Angle: