Page 1 - 3. LESSON NOTES-(ISOTOPES AND ISOBARS)
P. 1
SAI International School
Lesson Notes
Subject-Chemistry
Ch-Structure of atom
Topic- Isotopes and isobars
Isotopes
As we all know that atoms are made up of electrons, protons, and neutrons. The
nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons and the electrons revolve around the
nucleus. Atomic mass is the sum of some protons and the number of neutrons and
atomic number is equal to the number of protons. In an element, the number of
protons is always the same, but the number of neutrons keeps on changing.
Isotopes are the atoms in which the number of neutrons differs and the number of
protons is the same. From the above definition of atomic mass and the atomic
number, we can conclude that isotopes are those elements having the same atomic
number and different mass number.
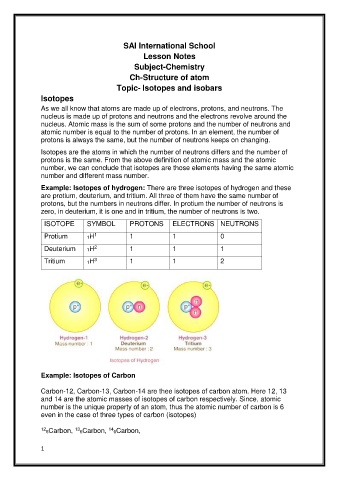
Example: Isotopes of hydrogen: There are three isotopes of hydrogen and these
are protium, deuterium, and tritium. All three of them have the same number of
protons, but the numbers in neutrons differ. In protium the number of neutrons is
zero, in deuterium, it is one and in tritium, the number of neutrons is two.
ISOTOPE SYMBOL PROTONS ELECTRONS NEUTRONS
1
Protium 1H 1 1 0
Deuterium 1H 1 1 1
2
3
Tritium 1H 1 1 2
Example: Isotopes of Carbon
Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14 are thee isotopes of carbon atom. Here 12, 13
and 14 are the atomic masses of isotopes of carbon respectively. Since, atomic
number is the unique property of an atom, thus the atomic number of carbon is 6
even in the case of three types of carbon (isotopes)
12 6Carbon, 13 6Carbon, 14 6Carbon,
1