Page 1 - 3.Lesson Note-Distillation, Frac distillation, crystallisation
P. 1
SAI International School
Subject-Chemistry
Ch-Is Matter around us pure?
Topic-Distillation, fractional distillation and crystallisation
LESSON NOTE
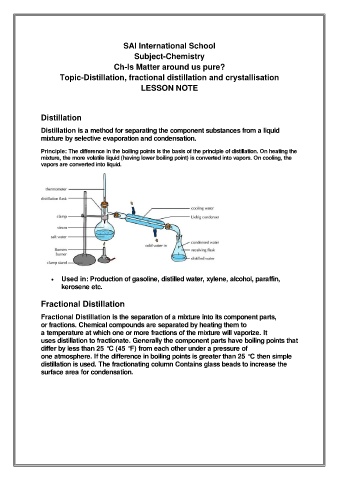
Distillation
Distillation is a method for separating the component substances from a liquid
mixture by selective evaporation and condensation.
Principle: The difference in the boiling points is the basis of the principle of distillation. On heating the
mixture, the more volatile liquid (having lower boiling point) is converted into vapors. On cooling, the
vapors are converted into liquid.
• Used in: Production of gasoline, distilled water, xylene, alcohol, paraffin,
kerosene etc.
Fractional Distillation
Fractional Distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts,
or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to
a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It
uses distillation to fractionate. Generally the component parts have boiling points that
differ by less than 25 °C (45 °F) from each other under a pressure of
one atmosphere. If the difference in boiling points is greater than 25 °C then simple
distillation is used. The fractionating column Contains glass beads to increase the
surface area for condensation.