Page 1 - 2.Lesson Notes -Sexual mode of reproduction IV
P. 1
SAI International School
Subject- Biology, Class-VII
Topic-Reproduction in Plants
Subtopic- Sexual mode of reproduction III -
Seed dispersal and its significance
Module-30
Lesson Notes
Seed dispersal and its significance
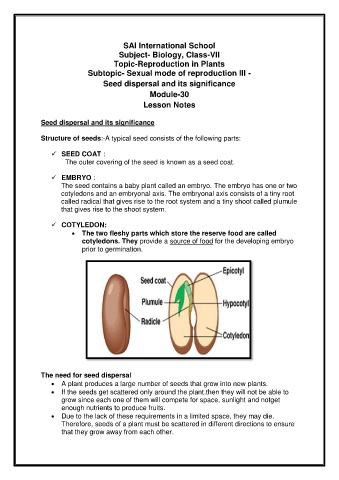
Structure of seeds:-A typical seed consists of the following parts:
SEED COAT :
The outer covering of the seed is known as a seed coat.
EMBRYO :
The seed contains a baby plant called an embryo. The embryo has one or two
cotyledons and an embryonal axis. The embryonal axis consists of a tiny root
called radical that gives rise to the root system and a tiny shoot called plumule
that gives rise to the shoot system.
COTYLEDON:
The two fleshy parts which store the reserve food are called
cotyledons. They provide a source of food for the developing embryo
prior to germination.
The need for seed dispersal
A plant produces a large number of seeds that grow into new plants.
If the seeds get scattered only around the plant,then they will not be able to
grow since each one of them will compete for space, sunlight and notget
enough nutrients to produce fruits.
Due to the lack of these requirements in a limited space, they may die.
Therefore, seeds of a plant must be scattered in different directions to ensure
that they grow away from each other.