Page 3 - LN-11
P. 3
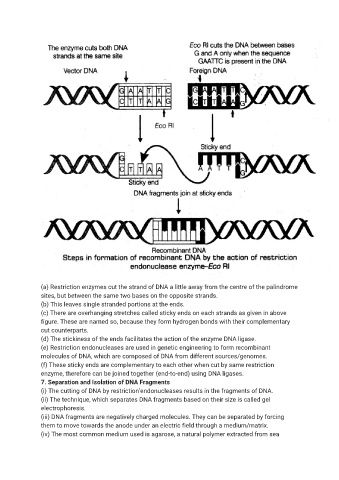
(a) Restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindrome
sites, but between the same two bases on the opposite strands.
(b) This leaves single stranded portions at the ends.
(c) There are overhanging stretches called sticky ends on each strands as given in above
figure. These are named so, because they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary
cut counterparts.
(d) The stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
(e) Restriction endonucleases are used in genetic engineering to form recombinant
molecules of DNA, which are composed of DNA from different sources/genomes.
(f) These sticky ends are complementary to each other when cut by same restriction
enzyme, therefore can be joined together (end-to-end) using DNA ligases.
7. Separation and Isolation of DNA Fragments
(i) The cutting of DNA by restriction’endonucleases results in the fragments of DNA.
(ii) The technique, which separates DNA fragments based on their size is called gel
electrophoresis.
(iii) DNA fragments are negatively charged molecules. They can be separated by forcing
them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium/matrix.
(iv) The most common medium used is agarose, a natural polymer extracted from sea