Page 4 - ln-ch-7
P. 4
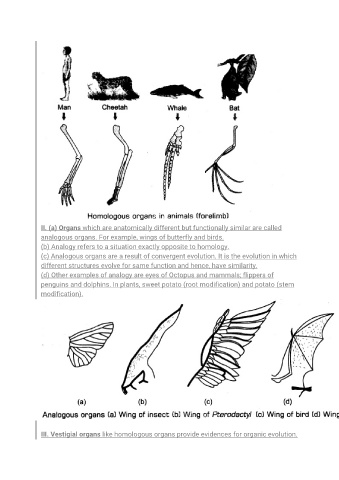
II. (a) Organs which are anatomically different but functionally similar are called
analogous organs. For example, wings of butterfly and birds.
(b) Analogy refers to a situation exactly opposite to homology.
(c) Analogous organs are a result of convergent evolution. It is the evolution in which
different structures evolve for same function and hence, have similarity.
(d) Other examples of analogy are eyes of Octopus and mammals; flippers of
penguins and dolphins. In plants, sweet potato (root modification) and potato (stem
modification).
III. Vestigial organs like homologous organs provide evidences for organic evolution.