Page 1 - Microsoft Word - Lesson note-1(biomolecules)
P. 1
SUBJECT-CHEMISTRY
CHAPTER-BIOMOLECULES.
Carbohydrates: they are a class of compounds which include polyhydroxy aldehydes
and and polydydroxy ketones.
Monosaccharides: They are soluble in water. These include non-hydrolysable
carbohydrates e.g. glucose, fructose.
Disaccharides: Which on hydrolysis give two molecules of monosaccharides e.g. cane
sugar, maltose, lactose.
Oligosaccharides: The carbohydrates on hydrolysis give 2-10 monoaccharides on
hydrolysis e.g. starch, amylase, amylopctin, glycogen, cellutos etc.
Sugars: include monosaccharides and oligosoaccharides.
Non sugar: starch, cellulose etc.
Reducing sugars: Those carbohydrates which contain free aldehydic or ketonic group
and reduce fehling’s solution and Tollen’s reagent are known as reducing sugar e.g.
maltose.
Non-reducing sugars: Those carbohydrates which do not have free aldehydic or
ketonic group and do not reduce Fehling’s solution and Tollen’s reagent are know as
non-reducing sugar e.g. sucrose.
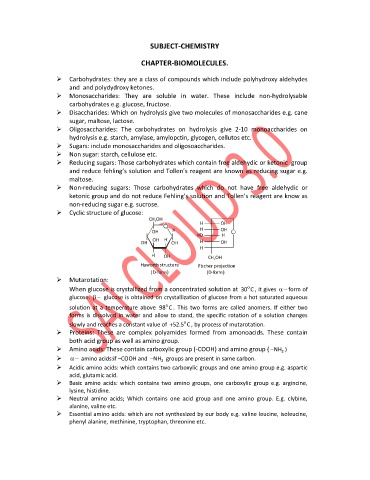
Cyclic structure of glucose:
Mutarotation:
o
When glucose is crystallized from a concentrated solution at 30 C , it gives form of
glucose. glucose is obtained on crystallization of glucose from a hot saturated aqueous
o
solution at a temperature above 98 C . This two forms are called anomers. If either two
forms is dissolved in water and allow to stand, the specific rotation of a solution changes
o
slowly and reaches a constant value of 52.5 C , by process of mutarotation.
Proteins: These are complex polyamides formed from amonoacids. These contain
both acid group as well as amino group.
Amino acids: These contain carboxylic group (-COOH) and amino group ( NH )
2
amino acids:if –COOH and NH groups are present in same carbon.
2
Acidic amino acids: which contains two carboxylic groups and one amino group e.g. aspartic
acid, glutamic acid.
Basic amino acids: which contains two amino groups, one carboxylic group e.g. argincine,
lysine, histidine.
Neutral amino acids; Which contains one acid group and one amino group. E.g. clybine,
alanine, valine etc.
Essential amino acids: which are not synthesized by our body e.g. valine leucine, isoleucine,
phenyl alanine, methinine, tryptophan, threonine etc.