Page 2 - H. A Producer's equilibrium
P. 2
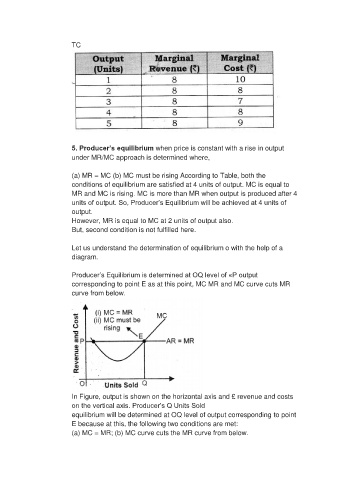
TC
5. Producer’s equilibrium when price is constant with a rise in output
under MR/MC approach is determined where,
(a) MR = MC (b) MC must be rising According to Table, both the
conditions of equilibrium are satisfied at 4 units of output. MC is equal to
MR and MC is rising. MC is more than MR when output is produced after 4
units of output. So, Producer’s Equilibrium will be achieved at 4 units of
output.
However, MR is equal to MC at 2 units of output also.
But, second condition is not fulfilled here.
Let us understand the determination of equilibrium o with the help of a
diagram.
Producer’s Equilibrium is determined at OQ level of «P output
corresponding to point E as at this point, MC MR and MC curve cuts MR
curve from below.
In Figure, output is shown on the horizontal axis and £ revenue and costs
on the vertical axis. Producer’s Q Units Sold
equilibrium will be determined at OQ level of output corresponding to point
E because at this, the following two conditions are met:
(a) MC = MR; (b) MC curve cuts the MR curve from below.