Page 3 - LN- EXCRETION
P. 3
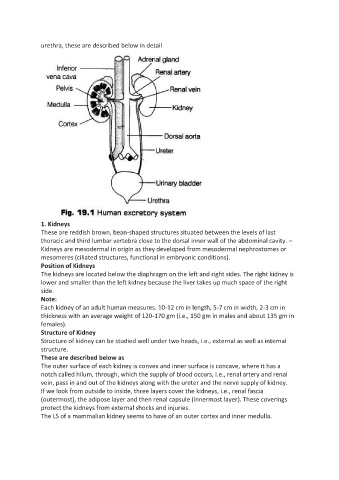
urethra, these are described below in detail
1. Kidneys
These are reddish brown, bean-shaped structures situated between the levels of last
thoracic and third lumbar vertebra close to the dorsal inner wall of the abdominal cavity. –
Kidneys are mesodermal in origin as they developed from mesodermal nephrostomes or
mesomeres (ciliated structures, functional in embryonic conditions).
Position of Kidneys
The kidneys are located below the diaphragm on the left and right sides. The right kidney is
lower and smaller than the left kidney because the liver takes up much space of the right
side.
Note:
Each kidney of an adult human measures. 10-12 cm in length, 5-7 cm in width, 2-3 cm in
thickness with an average weight of 120-170 gm (i.e., 150 gm in males and about 135 gm in
females).
Structure of Kidney
Structure of kidney can be studied well under two heads, i.e., external as well as internal
structure.
These are described below as
The outer surface of each kidney is convex and inner surface is concave, where it has a
notch called hilum, through, which the supply of blood occurs, i.e., renal artery and renal
vein, pass in and out of the kidneys along with the ureter and the nerve supply of kidney.
If we look from outside to inside, three layers cover the kidneys, i.e., renal fascia
(outermost), the adipose layer and then renal capsule (innermost layer). These coverings
protect the kidneys from external shocks and injuries.
The LS of a mammalian kidney seems to have of an outer cortex and inner medulla.